Definition of Natural Farming
“Natural Farming is a chemical-free traditional farming method. It is considered as an agroecology based diversified farming system which integrates crops, trees and livestock with functional biodiversity”.
Natural farming is a system where the laws of nature are applied to agricultural practices.
This method works along with the natural biodiversity of each farmed area, encouraging the complexity of living organisms, both plants, and animals that shape each particular ecosystem to thrive along with food plants.
Natural Farming builds on natural or ecological processes that exist in or around farms.
Natural Farming holds the promise of enhancing farmers’ income while delivering many other benefits, such as restoration of soil fertility and environmental health, and mitigating and/or reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
can be achieved through following specific principles:
- Adoption of diversified cropping system-based agriculture
- Recycling of naturally available nutrients in fields
- Recycling of on-farm generated biomass
- Use of locally developed and refined practices based on plant, animal and microbial source as raw materials
- Innovative practices continuously evolve on the field of farmers based on the cropping pattern, local climatic conditions, altitude, soil quality, severity and variability of insects and pests etc.
Features of Natural Farming
- According to natural farming principles, plants get 98% of their supply of nutrients from the air, water, and sunlight. And the remaining 2% can be fulfilled by good quality soil with plenty of friendly microorganisms. (Just like in forests and natural systems)
- The soil is always supposed to be covered with organic mulch, which creates humus and encourages the growth of friendly microorganisms.
- Farm made bio-cultures named ‘Jeevamrit, Beejamrit etc.’ are added to the soil instead of any fertilizers to improve microflora of soil. Jeevamrit, Beejamrit are derived from very little cow dung and cow urine of desi cow breed.
- It holds the promise of enhancing farmers’ income while delivering many other benefits, such as restoration of soil fertility and environmental health, and mitigating and/or reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- The system requires cow dung and cow urine (Gomutra) obtained from Indian breed cow only. Desi cow is apparently the purest as far as the microbial content of cow dung, and urine is considered.
- In natural farming, neither chemical nor organic fertilizers are added to the soil. In fact, no external fertilizers are added to soil or given to plants whatsoever.
- In natural farming, decomposition of organic matter by microbes and earthworms is encouraged right on the soil surface itself, which gradually adds nutrition in the soil, over the period.
- In natural farming there is no ploughing, no tilling of soil and no fertilizers, and no weeding is done just the way it would be in natural ecosystems.
- Natural, farm-made pesticides like Dashparni ark and Neem Astra are used to control pests and diseases.
- Weeds are considered essential and used as living or dead mulch layer.
- multi-cropping is encouraged over single crop method.
Principles of Natural Farming
A healthy soil microbiome is critical for optimal soil health and plant health, and thereby animal health and human health. Soil may be covered with crops for maximum period of the year.
The soil across a farm or larger field/collection of fields should have diverse crops, a minimum of 8 crops over the year.
Minimal disturbance of soils is critical; hence no till farming or shallow tillage is recommended.
Animals should be incorporated into farming.
Integrated farming systems are critical for promoting Natural farming. Bio stimulants are necessary to catalyze this process.
There are different ways of making bio stimulants. In India, the most popular bio-stimulants are based on fermentation of animal dung and urine, and uncontaminated soil. Increasing the amount and diversity of organic residues returned to the soil is very important.
These include crop residues, cow-dung, compost, etc. Pest management should be done through better agronomic practices (as enshrined in Integrated Pest management) and through botanical pesticides (only when necessary).
Use of synthetic fertilizers and other biocides is harmful to this process of regeneration and is not allowed.
As per the farmers who are regularly practising natural farming,the following practices has been considered as the most important components of Natural Farming;
Beejamrit.
Jivamrit.
Mulching.
Whapasa.
Scope of Natural Farming
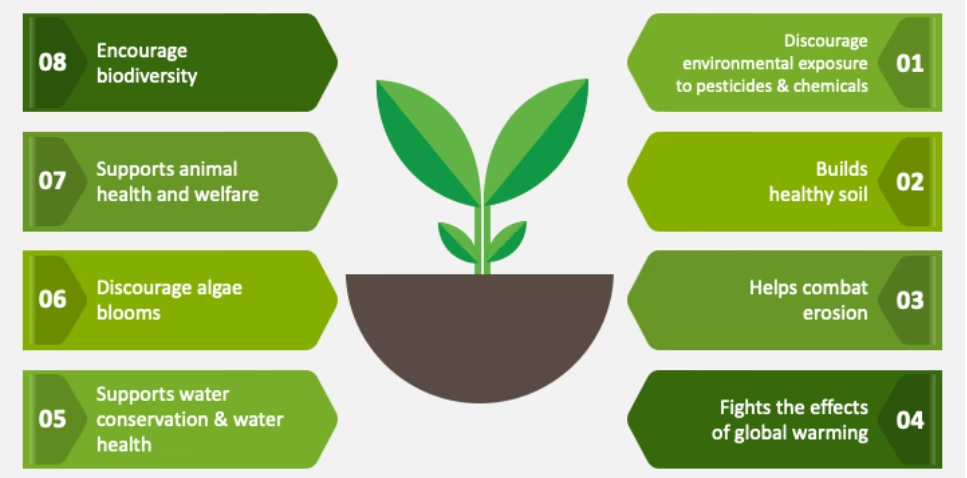
There are many working models of natural farming all over the world, the zero budget natural farming (ZBNF) is the most popular model in India. Natural Farming improves soil fertility, environmental health as well as helps in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and also promises the enhancement of farmer’s income.
In broad terms, Natural Farming can be considered as a prominent strategy to save the planet Earth for future generations.
It has the potential to manage the various farmland practices and hence sequester the atmospheric carbon in the soils and plants, to make it available for plants.
Importance of Natural Farming
Several studies have reported the effectiveness of natural farming in terms of increase in production, sustainability, saving of water use, improvement in soil health and farmland ecosystem.
It is considered as a cost- effective farming practices with scope for raising employment and rural development.
Natural Farming offers a solution to various problems, such as food insecurity, farmers’ distress, and health problems arising due to pesticide and fertilizer residue in food and water, global warming, climate change and natural calamities.
It also has the potential to generate employment, thereby stemming the migration of rural youth.
Natural Farming, as the name suggests, is the art, practice and, increasingly, the science of working with nature to achieve much more with less.
Benefits of Natural Farming
Improve Yield: Farmers practicing Natural Farming reported similar yields to those following conventional farming. In several cases, higher yields per harvest were also reported.
Ensures Better Health: As Natural Farming does not use any synthetic chemicals, health risks and hazards are eliminated. The food has higher nutrition density and therefore offers better health benefits.
Environment Conservation: Natural Farming ensures better soil biology, improved agro-biodiversity and a more judicious usage of water with much smaller carbon and nitrogen footprints.
Increased Farmers’ Income: Natural Farming aims to make farming viable and aspirational by increasing net incomes of farmers on account of cost reduction, reduced risks, similar yields, incomes from intercropping.
Employment Generation: Natural farming generates employment on account of natural farming input enterprises, value addition, marketing in local areas, etc. The surplus from natural farming is invested in the village itself.
Reduced Water Consumption: By working with diverse crops that help each other and cover the soil to prevent unnecessary water loss through evaporation, Natural Farming optimizes the amount of ‘crop per drop’.
Minimized Cost of Production: Natural Farming aims to drastically cut down production costs by encouraging farmers to prepare essential biological inputs using on-farm, natural and homegrown resources.
Eliminates Application of Synthetic Chemical Inputs: The overuse of synthetic fertilizers, especially urea, pesticides, herbicides, weedicides etc. alters soil biology and soil structure, with subsequent loss of soil organic carbon and fertility.
Rejuvenates Soil Health: The most immediate impact of Natural Farming is on the biology of soil—on microbes and other living organisms such as earthworms. Soil health depends entirely on the living organisms in it.
Livestock Sustainability: The integration of livestock in the farming system plays an important role in Natural farming and helps in restoring the ecosystem. Eco-friendly bio-inputs, such as Jeevamrit and Beejamrit, are prepared from cow dung and urine, and other natural products.
Many states have taken up initiatives for natural farming promotion Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu are among the leading states. As of now more than 10 lakh ha. area is covered under natural farming in India.
National Mission on natural farming
India launched the National Mission on Natural Farming to improve crop diversity and soil health, reduce farming costs and provide safe food to consumers.
- It aims to promote chemical-free farming.
- Natural farming involves local sourcing of inputs such as livestock manure and preparing biopesticides from herbs.
- It relies on traditional knowledge and seeks to improve soil health and push farmers to diversify the crop basket.
- With an outlay of ₹2,481 crore, the mission targets to reach 10 million farmers and cover 750,000 hectares in two years.
- To support farmers in 15,000 clusters, 10,000 bio-input resource centres will be set up.
- Farmers will receive hands-on training at model farms and 30,000 krishi sakhis will be deployed as community resource persons.
How do natural and organic farming differ?
In principle, the two forms of farming are the same. But organic farming follows stringent procedures and third-party certification, and requires a minimum conversion period of two to three years to shift from chemical to bio inputs. In natural farming, growers can decide on the pace to transition away from chemical fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring no sudden drop in yields.
This offers farmers flexibility and allows them to experiment with local inputs. On the flip side, while organic produce fetches premium price as it is certified, natural farm produce may be difficult to market as it is not certified.
How much area is under natural and organic farms?
About 0.65 million hectares (ha) is under natural farming across states, while 4.5 million ha is under organic farming, according to government data. Together, both make up less than 4% of the total crop area.
So, in addition to exports, there is an untapped potential as consumers shift to low-chemical residue produce. But bio-inputs and marketing are challenges.
Will a shift to natural farming lower yields?
A 2023 study by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research conducted in Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Karnataka found crop yields to be higher with use of farm yard manure (decomposed cow dung, urine, and fodder) compared with conventional farming. In Andhra, paddy yield under natural farming was 4% higher, while costs were about 5% lower. Farmers also received a small price premium. However, yields were lower for sugarcane and black gram. The study called for more scientific evidence.
What’s the science of natural farming?
It works on the principle that there is no shortage of nutrients in soil, air and water, and a healthy soil biology can unlock these nutrients. A bio-stimulant is prepared by fermenting dung with cow urine, jaggery and pulses flour.
This solution increases the microbial count in the soil, supplying plants with essential nutrients, besides making the soil porous and airy, and improving its water-holding capacity. Crop residues also prevent weeds. And multiple crops in the same field improve soil fertility.
Source: Mint