A tiger reserve is a protected area of land that is dedicated to the conservation of tigers and their habitats. Tiger reserves are established under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and are managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Conservation of Tiger (Panthera Tigris)
1. The IUCN status of the tiger is endangered, and it is protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
2. India has been actively collaborating with neighbouring countries to enhance transboundary conservation efforts like India-Bangladesh to promote tiger conservation across the Sundarbans landscape.
3. International Big Cats Alliance (IBCA) was launched by the Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, in 2023 to promote the protection of seven big cats: the tiger, leopard, snow leopard, lion, cheetah, puma and jaguar during a program honouring 50 years of Project Tiger. The alliance seeks to establish contact with a spectrum of countries that surround these large cats’ native habitats. The IBCA aims to increase international collaboration and conservation efforts for these untamed inhabitants.
Conservation Assured Tiger Standards (CA|TS) Accreditation
It is an international accreditation system that assesses management techniques in tiger reserves to make sure they adhere to strict conservation guidelines.
Project Tiger
1. The ‘Project Tiger’ is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) launched by the Central government on April 1, 1973, in a bid to promote conservation of the tiger. The programme came at a time when India’s tiger population was rapidly dwindling. According to reports, while there were 40,000 tigers in the country at the time of the Independence, they were soon reduced to below 2,000 by 1970 due to their widespread hunting and poaching.
2. To tackle the problem of hunting and poaching of not just tigers but also other animals and birds, then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi promulgated the Wildlife Protection Act in 1972. A year later, after a task force urged the government to create a chain of reserves dedicated to tiger preservation, government unveiled Project Tiger.
3. Launched at the Jim Corbett National Park, the programme was initially started in nine tiger reserves of different States such as Assam, Bihar, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal, covering over 14,000 sq km.
4. Notably, Project Tiger didn’t just focus on the conservation of the big cats. It also ensured the preservation of their natural habitat as tigers are at the top of the food chain.
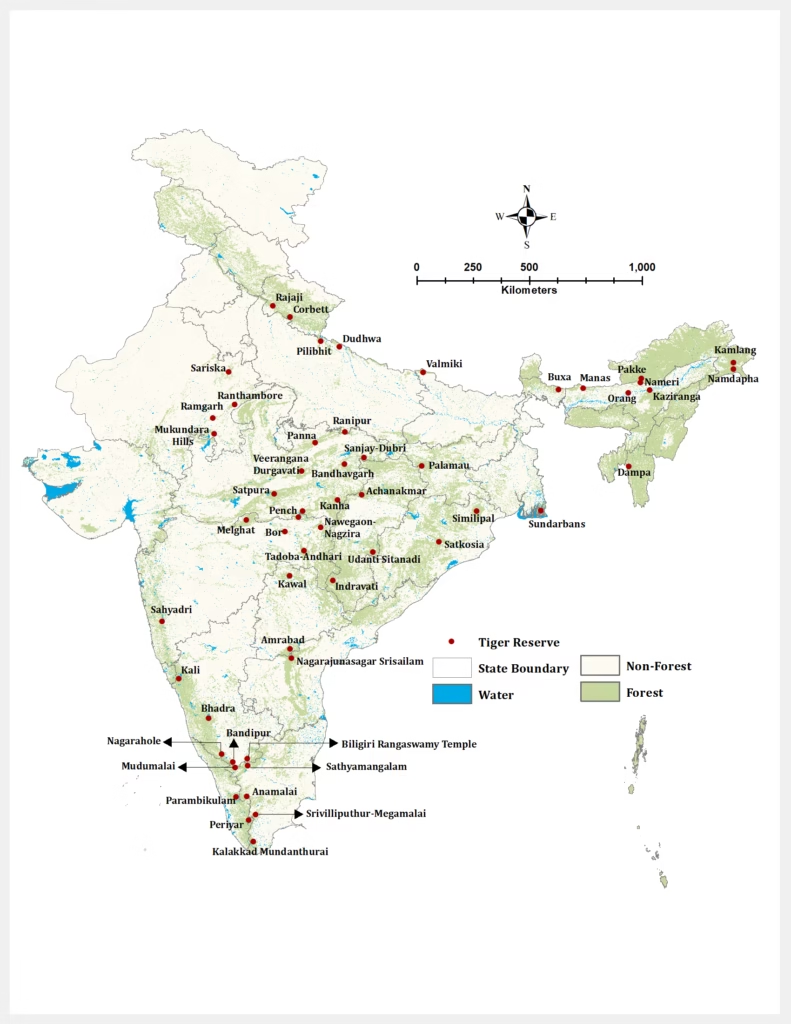
List of Tiger Reserves in India (As of December 2024)
| Tiger Reserves in India | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sl No | Tiger Reserve (TR) | State | TR Notification Year |
| 1 | Bandipur | Karnataka | 2007 |
| 2 | Corbett | Uttarakhand | 2010 |
| Amanagarh buffer | Uttar Pradesh | 2012 | |
| 3 | Kanha | Madhya Pradesh | 2007 |
| 4 | Manas | Assam | 2008 |
| 5 | Melghat | Maharashtra | 2007 |
| 6 | Palamau | Jharkhand | 2012 |
| 7 | Ranthambore | Rajasthan | 2007 |
| 8 | Simlipal | Orissa | 2007 |
| 9 | Sunderban | West Bengal | 2007 |
| 10 | Periyar | Kerala | 2007 |
| 11 | Sariska | Rajasthan | 2007 |
| 12 | Buxa | West Bengal | 2009 |
| 13 | Indravati | Chattisgarh | 2009 |
| 14 | Namdapha | Arunachal Pradesh | 1987 |
| 15 | Nagarjunsagar Sagar | Andhra Pradesh | 2007 |
| 16 | Dudhwa | Uttar Pradesh | 2010 |
| 17 | Kalakad Mundanthurai | Tamil Nadu | 2007 |
| 18 | Valmiki | Bihar | 2012 |
| 19 | Pench | Madhy Pradesh | 2007 |
| 20 | Tadobha Andhari | Maharashtra | 2007 |
| 21 | Bandhavgarh | Madhy Pradesh | 2007 |
| 22 | Panna | Madhy Pradesh | 2007 |
| 23 | Dampa | Mizoram | 2007 |
| 24 | Bhadra | Karnataka | 2007 |
| 25 | Pench – MH | Maharashtra | 2007 |
| 26 | Pakke | Arunachal Pradesh | 2012 |
| 27 | Nameri | Assam | 2000 |
| 28 | Satpura | Madhya Pradesh | 2007 |
| 29 | Anamalai | Tamil Nadu | 2007 |
| 30 | Udanti Sitanadi | Chattisgarh | 2009 |
| 31 | Satkoshia | Odisha | 2007 |
| 32 | Kaziranga | Assam | 2007 |
| 33 | Achanakmar | Chattisgarh | 2009 |
| 34 | Kali | Karnataka | 2007 |
| 35 | Sanjay Dhubri | Madhya Pradesh | 2011 |
| 36 | Mudumalai | Tamil Nadu | 2007 |
| 37 | Nagarhole | Karnataka | 2007 |
| 38 | Parambikulam | Kerala | 2009 |
| 39 | Sahyadri | Maharashtra | 2012 |
| 40 | Biligiri Ranganatha Temple | Karnataka | 2007 |
| 41 | Kawal | Telangana | 2012 |
| 42 | Sathyamangalam | Tamil Nadu | 2013 |
| 43 | Mukundara | Rajasthan | 2013 |
| 44 | Nawegaon Nagzira | Maharashtra | 2013 |
| 45 | Amrabad | Telangana | 2015 |
| 46 | Pilibhit | Uttar Pradesh | 2014 |
| 47 | Bor | Maharashtra | 2012 |
| 48 | Rajaji | Uttarakhand | 2015 |
| 49 | Orang | Assam | 2016 |
| 50 | Kamlang | Arunachal Pradesh | 2017 |
| 51 | Srivilliputhur Megamalai | Tamil Nadu | 2021 |
| 52 | Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve | Rajasthan | 2022 |
| 53 | Ranipur Tiger Reserve | Uttar Pradesh | 2022 |
| 54 | Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh | 2023 |
| 55 | Dholpur – Karauli Tiger Reserve | Rajasthan | 2023 |
| 56 | Guru Ghasidas – Tamor Pingla Tiger Resereve | Chhattisgarh | 2024 |
| 57 | Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary | Madhya Pradesh | 2024 |
Map of Tiger Reserves in India
Tiger Conservation Plan
As per the section 38 v (3) of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 The State Government shall prepare a Tiger Conservation Plan including staff development and deployment plan for the proper management of each area referred to in sub-section (1), so as to ensure—
(a) Protection of tiger reserve and providing tiger reserve specific habitat inputs for maintaining a viable population of tigers, co-predators and prey animals.
(b) Ecologically compatible land uses in tiger reserves and areas linking one Protected Area (PA) with another PA or tiger reserve for providing dispersal habitat and corridors.

